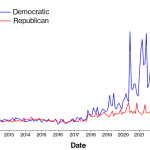
The impact of AI on the labor market is a topic garnering significant attention as new research highlights the profound changes ushered in by artificial intelligence. In a recent study, Harvard economists David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers emphasize how technological disruption is reshaping job roles, creating a dynamic environment of labor shifts. Notably, their research revealed patterns of occupational churn analysis illustrating that while periods of stability existed, a noticeable change has occurred from 2019 onward, suggesting AI workforce changes are at play. As AI continues to infiltrate various sectors, it raises critical questions about the future of work technology, pushing professionals and employers alike to adapt to these evolving demands. This wave of innovation could redefine not only job functions but also the very nature of employment across the economy, as evidenced by trends towards higher-paid STEM occupations and the decline of low-paid service jobs.
Exploring the influence of advanced technology on employment dynamics, we enter an era defined by artificial intelligence and its revolutionary effects on job markets. Terms such as job transformation and workforce evolution encapsulate the shifts seen in numerous occupations, where traditional roles are increasingly being replaced by machine capabilities. Economists have noted significant alterations in job distribution and security as technological advancements continue to disrupt established practices. The trend of automation not only evokes debates regarding job loss but also highlights the emergence of new skill demands and opportunities. As we analyze the trajectory of the labor landscape, it becomes evident that understanding the ramifications of such technological advancements is crucial for future work preparedness.
Understanding AI’s Influence on the Labor Market
As we navigate the evolving dynamics of the labor market, it is vital to examine the profound impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on job structures and workforce composition. The emergence of AI technologies signals a transformative phase for industries worldwide, leading to significant labor shifts and occupational churn. A recent study highlights that between 2019 and 2024, a noticeable increase in STEM jobs can be observed, with nearly 50% growth, further emphasizing how AI is reshaping the workforce landscape. Researchers are increasingly drawing attention to the ‘technological disruption jobs’ phenomenon, where innovative tools and systems redefine not only the skills required but also the nature of work itself.
Moreover, this AI-infused ecosystem leads to heightened competition among workers for high-skilled positions, underscoring the importance of continuous learning and adaptation. The integration of automation in various sectors evidences a clear trend where companies prioritize employees adept in technology, thus enhancing productivity. Hence, understanding AI’s influence is crucial for employees aspiring to thrive in a landscape marked by rapid advancements and shifting demands.
The ongoing technological advancements heralded by AI extend beyond mere tool enhancements; they provoke a cascade of changes within the job market. For instance, while previously entrenched roles, such as certain low-skilled jobs, suffer declines, there is an acute rise in the demand for technical talent capable of leveraging AI-driven solutions. This pivot towards high-skilled positions indicates a significant shift in the labor market, characterized by the uneven distribution of jobs that weigh heavily on expertise and adaptability. Economic analysts are now grappling with the implications of this trend on educational systems and workforce training, emphasizing the need for future-oriented strategies that cultivate a technologically skilled workforce.
The Future of Work: Navigating AI Workforce Changes
The phrase ‘future of work technology’ has garnered attention, particularly as AI continues to play a crucial role in shaping what work will look like in the coming decades. The findings of notable studies indicate a deviation from traditional employment patterns, notably the substitution of manual labor with smart technologies capable of performing tasks with greater efficiency and accuracy. This shift not only results in job displacement but also heralds new opportunities for innovation and growth in sectors focused on technological development. As organizations streamline processes through AI, they will likely see a restructuring of job roles that align more closely with emerging technological capabilities.
Consequently, companies are challenged to modify their hiring practices and organizational structures to accommodate these workforce changes. Employers must seek candidates who possess an aptitude for technology and are capable of engaging with AI systems. Furthermore, continuous training programs that focus on upskilling employees in AI competencies will become pivotal for long-term sustainability and competitive advantage. This evolving landscape marks a significant shift in how businesses will operate, fostering an environment where adaptability and technological literacy become paramount.
Moreover, the rise of AI technology necessitates a rethinking of traditional work roles and expectations, leading to the emergence of hybrid job designs combining human intelligence and AI capabilities. Workers now face the dual challenge of engaging with advanced technologies while maintaining core professional skills that foster creativity and interpersonal interactions. This evolution calls for an active response from both employees and educational institutions to cultivate a workforce resilient to the fluctuations in job requirements brought about by technological advancements.
Investments in AI-driven tools can vastly improve productivity, yet companies must tread carefully to ensure they do not neglect the human element that contributes significantly to creativity and problem-solving. As companies venture further into AI integration, the emphasis will increasingly shift toward creating synergistic roles that balance technology with human insight, ensuring that employees remain valuable even as the nature of work transforms.
Technological Disruption: Analyzing Employment Fluctuations
The study by Harvard economists sheds light on the historical context of labor market fluctuations aligned with technological disruptions, revealing patterns of occupational churn seen over the past century. Economists argue that the implications of AI on employment are not merely borne from automation anxiety but are reflective of larger trends mirroring past technological innovations. For instance, breakthrough technologies, such as electricity and computers, initially caused significant job losses, yet concurrently opened avenues for new job creation. The current narrative draws parallels with present AI advancements poised to induce similar patterns, indicating a phase of ‘technological disruption jobs’ that demands adaptation from the workforce.
As we assess fluctuations in employment, it becomes crucial to recognize that these transitions are precarious and often unpredictable, emphasizing the importance of a forward-thinking approach. Industries must prioritize adaptability and workforce resilience to navigate the complexities of AI-related labor transformations. Active engagement with data-driven assessments of employment trends allows organizations to proactively address potential skills gaps, preparing workers for an evolving landscape.
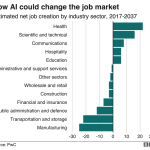
Furthermore, the analysis of occupational churn across various sectors points to critical insights about which jobs are at risk of displacement versus those likely to flourish in the AI era. For instance, the retail sector has witnessed a marked decline in employment due to the advent of e-commerce fueled by AI technologies. This trend illustrates the necessity for businesses to pivot and adopt strategies that integrate technology without compromising employment opportunities. Industries are encouraged to invest in workforce retraining aimed at transitioning affected workers into emerging roles while redefining current job functions to align with the demands of a technologically advanced landscape.
A nuanced understanding of technological disruption must inform policy discussions and economic strategy formulation to mitigate job loss impacts and foster an equitable transition for workers. For businesses, this may involve harnessing innovative technologies while simultaneously cultivating a resilient workforce capable of thriving amid such change, thereby maintaining a balance between progress and workforce integrity.
Occupational Churn: Assessing Long-term Trends
Occupational churn analysis reveals the ebb and flow of jobs in response to technological advancements over decades. The concept encompasses not only job losses but also the emergence of new roles that replace obsolete positions, illustrating the labor market’s adaptability amidst change. As noted in the findings of the Harvard study, the period of low employment churn observed between 1990 and 2017 provides a contrasting narrative against the back drop of burgeoning AI technologies that have begun reshaping job requirements and market demands. Understanding this trend is critical for assessing the health of the labor market and identifying the sectors poised for growth or decline.
Additionally, the statistics surrounding job replacements underscore the inevitability of workforce evolution as automation and AI redefine traditional job functions. The trend of high-wage, skilled positions growing while lower-paid jobs stagnate reinforces the need to align educational resources with the demands of an AI-driven economy. Addressing these challenges head-on through strategic workforce development initiatives will be crucial in managing the transition and harnessing the benefits of this occupational churn.
On a broader scale, the understanding of long-term trends in occupational churn offers insights into the socio-economic implications of AI technologies and the future of work. The research suggests that companies must not only adapt to changes brought forth by AI but also plan for a workforce that reflects these innovations. This necessitates institutions to acknowledge the shifting paradigms of job satisfaction, worker engagement, and career growth in creating sustainable employment opportunities. Without careful planning and consideration, gaps may arise that benefit some workers while sidelining others, further amplifying economic disparities.
Thus, the dialogue surrounding occupational churn should encompass both the opportunities and challenges posed by AI, preparing both workers and organizations to navigate a landscape characterized by unprecedented change. By fostering an inclusive approach, leveraging data insights, and enhancing worker training initiatives, stakeholders can contribute to a labor market geared towards resilience and innovation.
The Role of STEM Jobs in AI Transformation
The rapid rise of STEM jobs in recent years has underscored their pivotal role in the ongoing transformation of the labor market driven by AI technology. As reported, the share of STEM positions has increased significantly since 2010, as companies seek out individuals equipped with the advanced skills necessary to innovate and implement AI solutions. This trend highlights a distinct shift in hiring practices, where technical capacities are increasingly prioritized over traditional qualifications. Addressing this shift is essential for ensuring that the workforce is adequately prepared to meet the growing demands of the AI-driven economy.
Moreover, as AI continues to enhance productivity across various sectors, the competition for STEM talent intensifies. Organizations are not only ramping up their hiring efforts, but they are also realigning their investment strategies to nurture talent capable of driving the next wave of technological advances. By cultivating a solid pipeline of skilled workers, businesses can position themselves to succeed in an increasingly tech-centric market while simultaneously fostering innovation and adaptability.
The correlation between the growth in STEM jobs and advancements in AI indicates the interconnectedness of technology and education, necessitating a collaborative focus on both workforce preparation and technological integration. For educational institutions, this means enhancing curriculum offerings to include AI-related content and practical applications that resonate with industry needs. Additionally, training and continuous learning initiatives should emphasize a synergy between technical skills and creative problem-solving, preparing students to thrive in an environment characterized by rapid changes.
As the demand for STEM professionals surges, the implications for policy-makers are clear: fostering an ecosystem conducive to STEM education is paramount. Investments in education, mentorship programs, and partnerships between industry and academic institutions can significantly influence the future workforce. By prioritizing these areas, society can better equip individuals to pursue careers in technology and help bridge the gap created by AI, ensuring an inclusive approach to workforce transformation.
Long-term Effects of AI on Job Structures
The long-term effects of AI on job structures are still unfolding, but preliminary studies indicate a substantial shift in employment paradigms. As evidenced by historical occupational churn analysis, the patterns observed in past technological revolutions hint at similar disruptions brought on by AI advancements. As roles evolve and new occupations emerge, traditional job classifications may become increasingly irrelevant. Business leaders must adapt their strategies to accommodate these changes, recognizing that the landscape of work will continually shift as AI technologies become more integrated into daily operations.
Understanding these long-term effects requires a commitment to proactive workforce development initiatives. Organizations are challenged to invest in their employees’ continuous education, enhancing skill sets to align with evolving job requirements while ensuring that their workforce remains future-proof against ongoing technological advancements. A proactive approach to managing the implications of AI will be critical in mitigating disruption risks while maximizing the beneficial outcomes associated with these major transformations.
Additionally, the integration of AI into everyday work processes presents both opportunities and challenges for long-term employment rates. While some sectors may experience job growth fueled by AI, others may face contractions as specific tasks become automated. The balancing act lies in addressing the economic realities of displacement while innovating new roles that leverage human creativity and insight—qualities that AI cannot replicate. Companies must advocate for fluid job designs that highlight collaboration between humans and machines, capitalizing on the strengths of both to drive productivity and enhance job satisfaction.
In addressing the long-term implications of AI, stakeholders must consider the socio-economic landscape to ensure equality and inclusivity. Since technological advancements can exacerbate existing disparities, efforts must be made to include a diverse range of voices in conversations about the future workforce. This can be achieved by creating pathways for upskilling and retraining, thereby empowering individuals from various backgrounds to participate in the emerging job market effectively.
Preparing for Future Job Displacement and Creation
As we look toward the future, the narrative surrounding job displacement and creation due to AI necessitates a comprehensive strategy that considers both the potential for job loss and the opportunity for new roles to emerge. Understanding how technology will influence job availability guides businesses and workers in preparing for anticipated shifts in labor dynamics. With historical data indicating that technological disruptions have consistently led to job redefinitions, it is essential for workforce planning to adapt and align with the fast-paced changes that AI presents.
Furthermore, by affirming the importance of ongoing education and workforce agility, organizations can foster an environment where employees are well-prepared to transition into new roles that arise. Investing in retraining initiatives and educational partnerships can bridge skills gaps, helping workers transition seamlessly into emerging job markets. As AI continues to evolve, a proactive approach towards preparing for change must become industry standard.
Moreover, as workers face the threat of displacement, addressing the psychological impact associated with job loss becomes increasingly vital. Providing resources for emotional support, career counseling, and guidance will empower individuals to face the challenges posed by technology with resilience. By understanding the potential for job displacement alongside proactive efforts to create new opportunities, companies can establish a balanced narrative around the changes that AI brings.
Ultimately, building a robust framework for preparing for AI-induced job displacement involves collaboration across sectors—businesses, educational institutions, and government entities ought to work together to create an informed and equipped workforce ready to meet the demands of a rapidly changing job climate.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI impacting labor shifts in various industries?
AI is significantly impacting labor shifts across various industries by automating routine tasks and altering job roles. This technological disruption is leading to a demand for higher-skilled workers, particularly in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) sectors, which are witnessing a surge in job opportunities as employers prioritize technical talent to drive innovation.
What are the trends related to technological disruption and jobs?
Recent trends indicate that the U.S. labor market is experiencing notable changes due to technological disruption. Key trends include the end of job polarization, growth in high-skilled positions, an increase in STEM-related jobs, and a decline in low-paid service roles. These changes highlight how artificial intelligence is reshaping job distribution and employment dynamics in today’s economy.
What is occupational churn analysis in the context of AI’s influence on the labor market?
Occupational churn analysis measures the rate of job changes across various sectors over time. In the context of AI’s influence on the labor market, it reveals how AI-driven automation has accelerated disruptions in employment patterns, leading to shifts in job availability and the structural dynamics of various industries.
What are the potential impacts of AI on the future of work technology?
The future of work technology is being reshaped by AI, which is expected to enhance productivity and efficiency while also posing risks of job displacement for lower-skill roles. Companies will increasingly demand higher outputs from knowledge workers, pushing for an adaptation to AI tools to remain competitive in a changing labor landscape.
How does AI contribute to occupational shifts and the decline of certain job sectors?
AI contributes to occupational shifts by automating tasks traditionally performed by human workers, leading to a notable decline in sectors such as retail and low-paid service jobs. This transformation demonstrates a significant reduction in job shares, particularly in areas vulnerable to AI integration, with fewer positions available for routine, manual labor.
Are there any predictions about AI and job growth in the coming years?
Experts predict that AI will drive job growth particularly in high-skilled and technology-focused roles. While some job sectors may face reductions, the integration of AI technologies is expected to create new opportunities in fields requiring advanced training and expertise, reshaping the overall employment landscape.
What role do economists believe AI will play in structural changes to the workforce?
Economists believe AI will play a pivotal role in driving structural changes within the workforce. As AI technologies advance, they are transforming the nature of work and demand for labor, necessitating adjustments in skill sets and potentially leading to both economic growth and job displacement in different sectors.
What insights do studies provide about the relationship between AI investment and job distribution?
Studies suggest that significant investment in AI is already influencing job distribution across the economy. As organizations prioritize AI integration, there is a clear trend towards creating high-tech roles while also witnessing a decline in positions that are more easily automated, highlighting the need for an adaptive workforce.
How does the historical context of technological disruption inform current perceptions of AI’s impact on jobs?
The historical context of technological disruption provides a nuanced understanding of AI’s impact on jobs. While past disruptions led to fears of job loss, the recent analysis reveals a more complex scenario where AI might result in both job displacement and the emergence of new career opportunities, suggesting a need for workforce adaptability.
What strategies can workers adopt to navigate labor market changes driven by AI?
To navigate labor market changes driven by AI, workers should focus on acquiring new skills, particularly in technology and STEM fields. Continuous learning, adaptability, and upskilling can help individuals remain competitive and find opportunities in a rapidly evolving job market influenced by artificial intelligence.
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Job Polarization | Shift away from job polarization trends, with more high-paid jobs emerging and growth in skill-based employment. |
| Increase in STEM Jobs | STEM job share increased from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024, with significant investments in AI-related roles. |
| Decline in Low-Paid Service Jobs | Flat or declining employment in low-paid service jobs since 2019, potentially accelerated by AI and market conditions. |
| Reduction in Retail Sales Jobs | Retail sales jobs fell from 7.5% to 5.7% from 2013 to 2023, driven by e-commerce growth and AI integration. |
Summary
The AI impact on the labor market is becoming increasingly evident, as recent research indicates significant changes in job dynamics and industry trends. Notably, the evolution towards high-skilled, well-compensated positions in science and technology contrasts sharply with the decline of service sector jobs. Understanding these patterns helps highlight the dual nature of AI as a tool for productivity enhancements while also posing risks to job security in various fields. As we navigate this complex transition, it’s crucial for workers and businesses alike to adapt to the ongoing transformations dictated by artificial intelligence in the workforce.