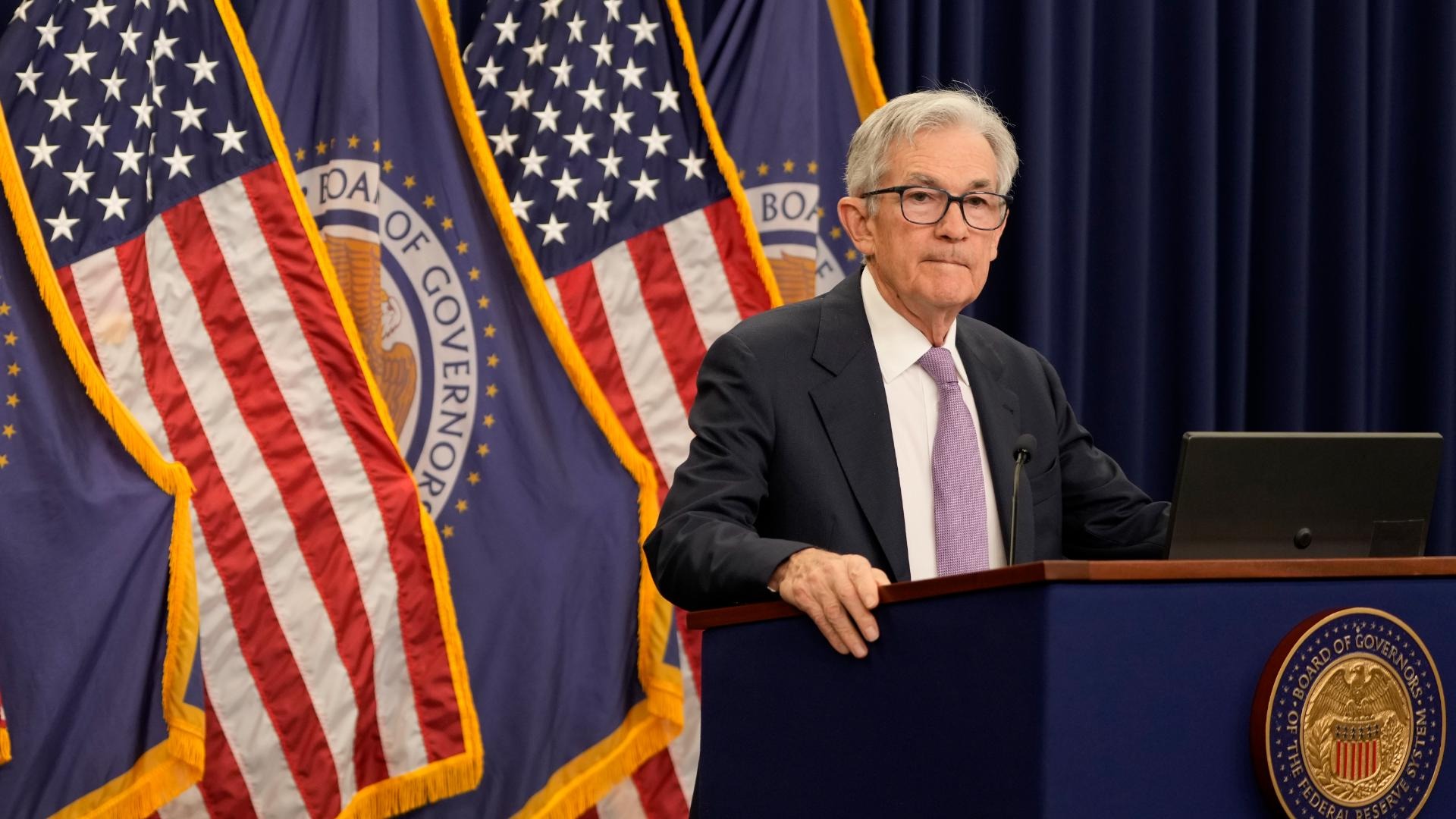
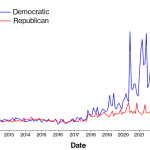
The recent Federal Reserve rate cut marks a significant shift in monetary policy, with the central bank reducing interest rates by half a percentage point—the first such decrease in four years. This decision aims to ease borrowing costs for consumers, potentially providing much-anticipated relief for credit card and mortgage holders alike. Economists predict this cut may stimulate economic growth, helping to alleviate consumer debt and bolster housing affordability amidst ongoing financial challenges. However, questions linger about how these adjustments in interest rates will impact individuals and the broader economy in the coming months. As the Federal Reserve navigates these changes, it continues to monitor inflation and labor market trends, indicating that further adjustments to the Federal Reserve policy may be on the horizon.
The recent adjustment in the Federal Reserve’s interest rate strategy, often referred to as a monetary easing, has caught the attention of financial analysts and consumers alike. This decisive action to lower borrowing costs is expected to influence various sectors of the economy, from housing markets to consumer lending rates. With the hope of promoting economic activity and mitigating the burdens of consumer debt, this rate reduction is a strategic move aimed to bolster confidence among borrowers and investors. As interest rates fluctuate, observers are keenly interested in how these changes will affect everything from mortgage rates to the overall economic impact on households. As we delve deeper into the ramifications of this Federal Reserve policy shift, understanding its implications for financial markets becomes increasingly crucial.
Understanding the Federal Reserve Rate Cut
The recent decision by the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates by 0.5 percentage points represents a meaningful shift in monetary policy. This reduction is the first in four years, and it aims to stimulate economic activity in various sectors, such as consumer lending and borrowing costs. The Fed’s action signals a proactive response to conditions in the economy, aiming to reduce the burden of consumer debt and encourage spending. By lowering the cost of borrowing, it is expected that consumer confidence will rise, motivating individuals to take on new loans for homes and cars.
Moreover, this rate cut can provide a more favorable environment for homebuyers grappling with high mortgage rates. As stated by economist Jason Furman, mortgage interest rates are likely to decrease further as the Fed maintains its easing policy. Such favorable adjustments can aid individuals in entering the housing market, addressing the affordability crisis that many potential buyers have been facing. Additionally, the Fed’s strategy may also influence Wall Street positively, as investors react to the enhanced liquidity in the economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a Federal Reserve rate cut mean for interest rates?
A Federal Reserve rate cut typically lowers interest rates across the board, making borrowing cheaper. This includes reductions in mortgage rates, personal loan rates, and credit card interest rates. When the Fed cuts rates, consumers can expect lower monthly payments on loans, fostering increased spending and investment in the economy.
How will the recent Federal Reserve rate cut impact mortgage rates?
The recent Federal Reserve rate cut is likely to contribute to lower mortgage rates. As the Fed eases its monetary policy, lenders are expected to adjust their rates downward, improving housing affordability for potential homebuyers. However, while the trend indicates lower rates, the extent of the decrease will depend on various market factors.
What are the potential economic impacts of the Federal Reserve’s rate cut on consumer debt?
The Federal Reserve’s rate cut can significantly impact consumer debt by lowering interest costs on credit cards and loans. As borrowing becomes cheaper, consumers may find relief from high-interest debt, allowing them to pay off balances more efficiently and increase disposable income, thereby stimulating further economic growth.
Will more Federal Reserve rate cuts follow, and what impacts could that have?
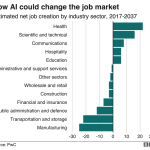
Experts suggest additional Federal Reserve rate cuts are likely in the near future, potentially around two more by year-end. These cuts could further lower interest rates and bolster economic activity, encouraging businesses to invest and consumers to spend, ultimately supporting job creation and economic growth.
How does the Federal Reserve rate cut affect the overall economy?
The Federal Reserve rate cut aims to stimulate economic growth by making borrowing cheaper for consumers and businesses. While it can lead to increased consumer spending and job creation, the balance is delicate, as too much easing can lead to higher inflation if not monitored carefully. The long-term impact will depend on inflation trends and market response.
When can consumers expect to see relief from high interest rates following a Federal Reserve rate cut?
While the Federal Reserve rate cut signals the potential for lower interest rates, consumers may experience a gradual decline in rates. It may take time for these cuts to translate into noticeable reductions in credit card and personal loan rates, and it’s expected that high rates could persist for several months before seeing significant relief.
Are there risks associated with the Federal Reserve rate cuts, particularly regarding inflation or economic stability?
Yes, while Federal Reserve rate cuts can stimulate economic growth, they also carry risks. If the economy overheats or inflation rises too quickly, it can create instability. The Fed must carefully monitor economic indicators to ensure that rate cuts do not lead to runaway inflation or economic imbalances.
What factors contribute to how quickly mortgage rates will decrease after a Federal Reserve rate cut?
Mortgage rates are influenced by various factors beyond just the Federal Reserve rate cut, including market expectations about future rate changes, overall economic conditions, and lending risk assessments. While a rate cut typically leads to reduced mortgage rates, the pace of decline can vary significantly depending on these factors.
How does the Federal Reserve rate cut affect financial markets and investor behavior?
A Federal Reserve rate cut often leads to increased investor confidence as lower borrowing costs can boost corporate profits. This can result in stock market rallies as investors anticipate better earnings prospects. However, reactions can vary based on perceptions of economic stability and future growth potential.
What should consumers keep in mind regarding Federal Reserve policy changes and their financial planning?
Consumers should stay informed about Federal Reserve policy changes as they can directly impact interest rates on loans and savings. It’s wise for individuals to assess their debt management strategies, consider refinancing options when rates drop, and plan for potential economic fluctuations resulting from these policies.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Federal Reserve Rate Cut | The Fed cut interest rates by 0.5 percentage points, the first reduction in four years. |
| Impact on Borrowing Costs | Consumers will benefit from lower borrowing costs, particularly credit card debts and mortgage rates. |
| Future Rate Cuts | The Fed may consider two additional cuts by the end of the year, contingent on economic data. |
| Economic Outlook | The Fed aims to balance slowing growth and inflation control while avoiding recession. |
| Expected Market Reaction | Market adjustments are anticipated in response to Fed signals on labor market changes. |
| Housing Market | Mortgage rates are expected to decrease, aiding housing affordability over time. |
| Consumer Debt Relief | Relief from high interest rates on debts such as credit cards may take time, likely remaining elevated for a year. |
Summary
The Federal Reserve rate cut is expected to provide significant relief for consumers, especially those with debt and potential home buyers. This strategic move aims to stimulate economic growth while managing inflation effectively. The implications include a lowering of mortgage rates and an uplift in job creation over the next year. However, the timeline for seeing substantial benefits remains uncertain, with high interest rates likely persisting in the short term. Overall, the Federal Reserve is keen on calibrating its policy to support both Wall Street and Main Street, indicating that the economy is on a path towards recovery.