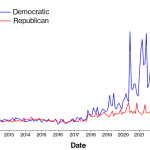
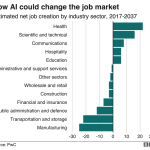
Generative AI adoption is rapidly transforming how we interact with technology in both our personal and professional lives. Since the introduction of ChatGPT in November 2022, nearly 40% of Americans have engaged with this groundbreaking technology, highlighting significant shifts in AI in the workplace. This swift embrace of generative AI, which surpasses the adoption rates of the internet and personal computers, underscores the urgency for businesses to understand its potential impact on jobs and the future of work with AI. As organizations begin to integrate AI tools into their operations, understanding technology adoption rates becomes crucial for developers and business leaders alike. The implications of generative AI usage could redefine industries, making it essential for stakeholders to leverage its capabilities effectively.
The swift uptake of creative AI solutions signifies a remarkable shift in technological engagement across various demographics. With tools like ChatGPT stepping into the mainstream, this new wave of artificial intelligence has begun to permeate both professional environments and everyday life. As users harness these innovations, it prompts critical discussions about the influence of this technology on workforce dynamics and job roles. The rapid technology integration is not just reshaping tasks but is also paving the way for a transformed landscape in the future of employment. In this context, understanding how generative AI tools are being utilized will be pivotal for companies looking to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving market.
The Rise of Generative AI Adoption
Generative AI adoption has surged at a pace unprecedented compared to earlier technological advancements like the internet and personal computers. A recent survey revealed that nearly 40 percent of Americans aged 18-64 have engaged with generative AI, showcasing its widespread acceptance across various demographics. The rapid normalization of tools like ChatGPT has sparked discussions about the transformative impact of AI in both professional and personal settings, indicating a paradigm shift in how technology is integrated into daily life.
This swift adoption highlights not only the accessibility of generative AI but also the societal readiness for such innovations. Unlike previous technologies, which took years to gain traction, generative AI is being embraced by younger generations who are often more tech-savvy and eager to leverage these tools for productivity. The implications for the future of work are profound, as organizations that adapt to these changes will likely find themselves at a competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the implications of generative AI adoption for technology in the workplace?
Generative AI adoption in the workplace signifies a transformative shift in how tasks are completed. As nearly 28% of employed adults utilize generative AI tools like ChatGPT for various job-related tasks, this technology enhances productivity, streamlines workflows, and fosters innovation. Businesses leveraging AI can improve efficiency and gain a competitive edge.
How does generative AI adoption compare to previous technology trends?
Generative AI is being adopted at a significantly faster rate than the internet and personal computers were during their early phases. About 40% of U.S. adults have engaged with generative AI, showcasing its rapid integration into everyday tasks, both at work and home, indicating a substantial shift towards tech reliance in modern economies.
What factors contribute to the speed of generative AI adoption in various demographics?
The swift adoption of generative AI can be attributed to existing technological infrastructures like personal computers and the internet, which facilitate access. Younger individuals and those with higher education levels tend to adopt generative AI more readily, reflecting a broader trend seen with other emerging technologies.
What tasks are most effectively enhanced by generative AI adoption in the workplace?
Generative AI proves particularly useful for tasks such as drafting emails, generating reports, conducting data analyses, and creating content. Its versatility allows employees across various sectors—from STEM to management—to enhance productivity by automating routine tasks.
What critical insights should executives take away about generative AI usage in their industries?
Executives should recognize that the rapid adoption of generative AI reflects a potential for significant economic impact similar to the rise of personal computers. Companies that proactively explore and integrate AI into their operations may develop competitive advantages, uncovering innovative applications that can drive growth.
How will the generative AI adoption influence the future of work?
The integration of generative AI into workplaces is set to redefine job roles, improve productivity, and spur creative problem-solving. As businesses embrace this technology, the future of work will likely require new skills and adaptability, emphasizing the importance of continuous learning in an AI-driven landscape.
What challenges might businesses face during the generative AI adoption process?
Businesses may encounter challenges such as integration complexities, employee training needs, and the need for updated policies regarding AI usage. Furthermore, concerns about data privacy and ethics in AI applications must be addressed adequately to ensure responsible and effective use.
How does generative AI adoption affect job security and the impact of AI on jobs overall?
Generative AI adoption can lead to job transformation rather than outright job loss, as it automates specific tasks but also creates opportunities for more strategic roles. While certain jobs may diminish, new skills and positions are likely to emerge, emphasizing the need for workforce reskilling and adaptability.
What role will technological adoption rates play in shaping the generative AI landscape?
Understanding technology adoption rates is crucial for forecasting generative AI’s economic impact. As significant engagement is observed, organizations need to strategize their AI initiatives, leveraging adoption patterns to optimize new solutions and meet market demands effectively.
What types of companies are likely to benefit most from adopting generative AI technologies?
Companies that innovate and leverage generative AI for operations, such as content creation, data processing, and customer engagement, stand to gain the most. Early adopters who harness AI’s versatility could drive long-term growth and profitability, echoing the advantages recognized in past technological evolutions.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Generative AI Adoption Rates | 40% of U.S. adults aged 18-64 have used generative AI, with 28% using it at work and 33% at home. |
| Speed of Adoption | Generative AI is being adopted faster than the internet and personal computers were in their early days. |
| Demographic Trends | Usage is higher among younger people, men, and those with higher education levels. |
| Use Across Occupations | Adoption varies by occupation, with higher rates in STEM and management fields. |
| Implications for Businesses | Businesses should consider the rapid adoption of generative AI for future growth and innovation. |
| Future Prospects | The potential for generative AI to become an essential tool for businesses in the next 5-10 years. |
Summary
Generative AI adoption is rapidly reshaping how Americans work and interact with technology. As demonstrated by recent studies showing near 40% usage among adults, this technology’s swift integration into workplaces and homes can significantly impact productivity and innovation. Organizations that embrace and leverage generative AI now stand to gain a competitive edge in the evolving economy, marking a pivotal transition reminiscent of the earlier revolutions brought on by personal computers and the internet.