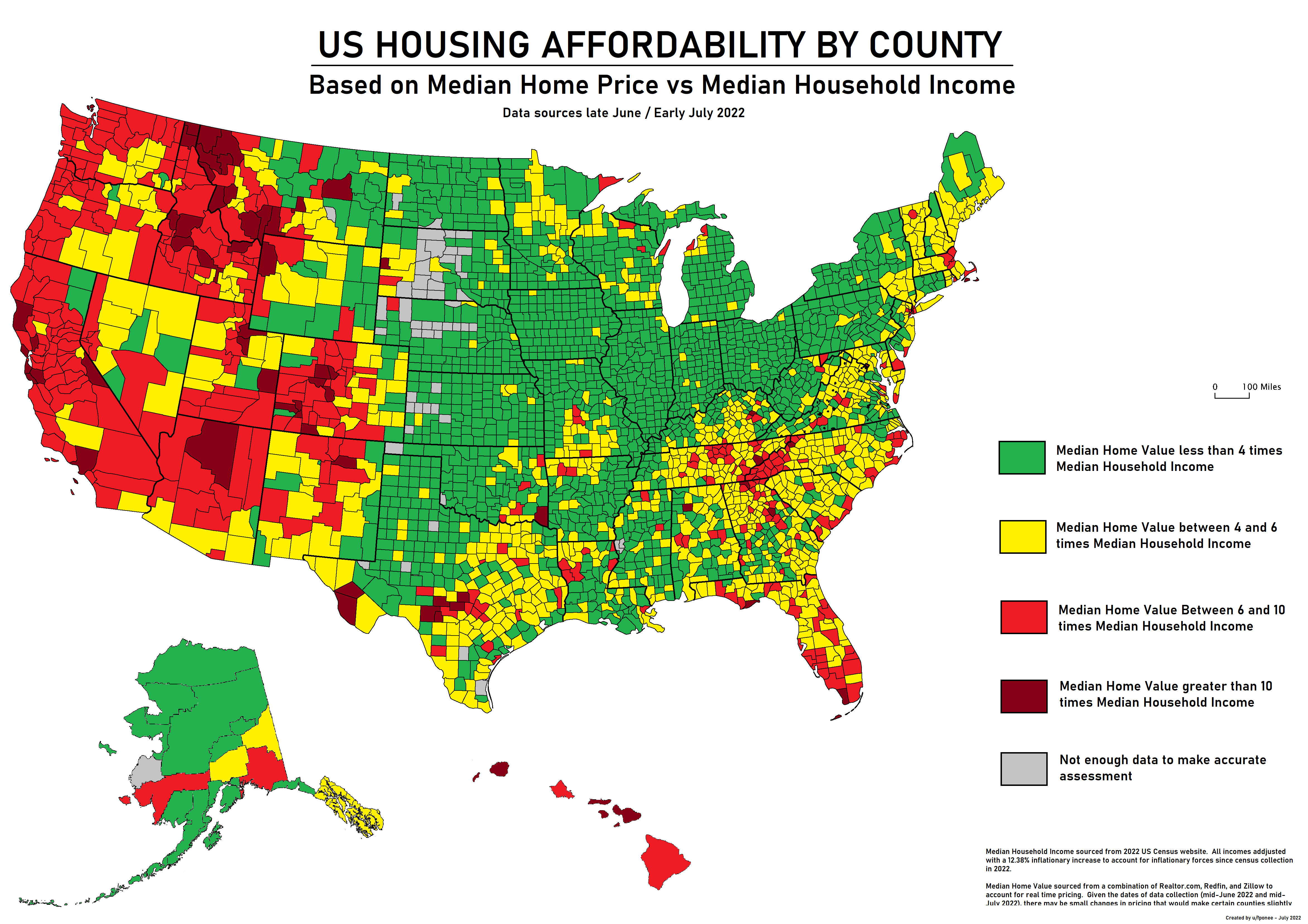
Housing affordability has become a pressing issue in the United States, as the dream of homeownership slips further from the grasp of many Americans. The skyrocketing costs of new single-family homes, which have more than doubled since 1960, are exacerbated by rising construction costs and restrictive land-use regulations. A growing body of research highlights how NIMBYism—the resistance to new housing developments in local communities—contributes to this housing crisis by limiting supply and stifling innovation in construction. These constraints not only inflate homeownership costs but also diminish productivity in the building sector, leading to smaller, less efficient construction firms. As the gap between housing prices and wages widens, the urgency to address housing affordability has never been more critical.
The challenge of affordable housing is intricately linked to the broader issues of market accessibility and residential costs. More aptly described as the struggle for affordable shelter, this dilemma emerges as local opposition to new developments leads to a significant reduction in available homes. Increasingly stringent land-use regulations curtail the ability of builders to innovate and respond to housing demands effectively. Such resistance, often termed NIMBYism, plays a pivotal role in escalating the homeownership expenses faced by prospective buyers. Understanding this complex interplay between local policies and construction productivity is vital for fostering an environment that encourages greater access to affordable housing.
The Impact of NIMBYism on Housing Development
NIMBYism, or ‘Not In My Backyard’ attitudes, significantly influence housing development in communities across the United States. This phenomenon arises when residents resist new construction projects, fearing that such developments will alter their neighborhood’s character or decrease property values. As a result, local governments often impose strict land-use regulations to appease these constituents, which inherently stifles innovative building practices and diminishes the scale of construction projects. When developers are forced to navigate a labyrinth of zoning laws, review boards, and possibly local referendums, the process of constructing homes becomes overly complicated and costly.
The cumulative effect of NIMBYism has led to a crisis in housing affordability. With fewer large-scale developments, the housing market sees a reduction in supply, driving up prices for new homes. Historical data shows that large builders were able to provide affordable housing through mass production techniques, producing thousands of homes on expansive tracts of land. Today, however, as restrictions tighten, smaller builders dominate the market—these firms lack the capacity and incentive to innovate or reduce costs, exacerbating the housing affordability issue for many Americans.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does NIMBYism affect housing affordability in the U.S.?
NIMBYism, or the ‘Not In My Backyard’ mentality, significantly contributes to housing affordability challenges by opposing new construction projects. This resistance leads to stricter land-use regulations, which can limit the availability of housing and drive up costs. As a result, homeownership becomes increasingly unattainable for many Americans.
What role do land-use regulations play in the housing crisis?
Land-use regulations are often cited as a major factor in the housing crisis, as they restrict the types and sizes of housing developments. These regulations can hinder construction productivity, leading to fewer homes being built, which exacerbates the issue of housing affordability.
In what ways is construction productivity related to housing affordability?
Construction productivity directly impacts housing affordability; when productivity is low, fewer homes are built, and those that are constructed tend to be more expensive. Enhancing construction productivity through innovative practices and scaling up housing projects could help alleviate the current housing crisis.
How has the cost of homeownership changed over the years?
The cost of homeownership has more than doubled since 1960, a trend driven by factors such as rising labor and material costs, as well as the impact of land-use regulations. This escalation in prices has made homeownership increasingly unreachable for many families.
What can be done to improve housing affordability amid current challenges?
To improve housing affordability, it is crucial to reform land-use regulations that limit large-scale housing projects. Encouraging higher construction productivity, investing in innovative building practices, and fostering a more open attitude towards new developments can help create more accessible housing options for all.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Housing Affordability Crisis | The U.S. faces a housing affordability crisis where housing ownership is increasingly out of reach for many. |
| Rising Costs | The price of new single-family homes has doubled since 1960, largely due to rising labor and material costs. |
| Impact of NIMBY Policies | Land-use regulations and NIMBYism limit the scale of housing projects, reducing overall construction productivity. |
| Loss of Productivity | Construction productivity has fallen by 40% from 1970 to 2000, diverging from improvements in other sectors like manufacturing. |
| Smaller Builders | The construction industry has shifted to smaller firms, which innovate less and build fewer homes efficiently. |
| Intergenerational Wealth Transfer | Younger generations are accumulating significantly less housing wealth compared to older ones, widening the wealth gap. |
| Historical Context | The decline in construction productivity began around 1970, at the same time that land-use regulations became more prevalent. |
| Architectural Innovation Lag | Despite historic levels of innovation in other sectors, construction innovation and patenting have decreased since the 1970s. |
Summary
Housing affordability remains a critical issue affecting millions in the United States today. With soaring home prices and restrictive land-use regulations, many Americans find homeownership increasingly unattainable. As highlighted in recent research, the combination of rising costs, smaller builders, and a lack of innovation due to NIMBY policies are key contributors to this crisis. To effectively address housing affordability, policymakers need to reevaluate land-use regulations and to promote larger-scale building projects that can drive down costs and enhance housing availability.